![[Picture]](semester%202%20test%20review_files/image002.jpg)
III. DNA Technology 5%
Define: homozygous
heterozygous
allele
trait
genotype
What is the difference between haploid and diploid?
What is the diploid number for a human cell?
Complete a Punnett square for a homozygous dominant individual crossed with a heterozygous individual.
In peas, tall height is dominant over short height and yellow pods are dominant over green pods. Do a double-trait cross for a tall plant with green pods (Ttgg) and a short plant with yellow pods (ttGg). Know how to do 16-square Punnett problems!!
For the pedigree below, could the condition be:
a. Autosomal recessive?
b. Automsomal dominant?
c. Sex-linked recessive?
![[Picture]](semester%202%20test%20review_files/image002.jpg)
A red flower (R R) is crossed with a white flower (W W).
d. If this is a case of codominance dominance, which phenotypes will the offspring display (and % of each):
e. If this is a case of incomplete dominance, which phenotypes will the offspring display (and % of each):
Give an example of a sex-linked trait in humans.
A mother is a carrier for hemophilia and a father doesn’t have hemophilia. What is the probability of the sons having hemophilia? What is the probability of their daughters having hemophilia?
Explain why it is more likely for a male to be colorblind than a female.
What is a transgenic organism?
What is gene splicing?
What is cloning?
In a gel electrophoresis, what is the function of the enzyme, gel and electricity?
If you had the sequence AAACGACTATTAGCAGAGCCT, what would a gel electrophoresis look like after digesting the sample with enzyme A (cuts after CGA) and after digesting the sample with enzyme B (cuts after TTA)?

![]()
![]()
Recall that the theory of evolution was not ‘invented’ by Charles Darwin (his contribution is the theory of natural selection, a means by which evolution can occur). The idea of evolution was around long before Darwin published his theory of natural selection is 1859.
Artificial selection influenced the ideas of Charles Darwin. He recognized that the process lead to organisms like homing pigeons and domestic dogs.
What is artificial selection?
State Darwin’s three main points (from notes):
1)
2)
3)
How did the peppered moths of England (maybe, remember some of original data was not reliable) provide evidence to support the theory of natural selection?
Define –
species:
gene pool:
population:
mutation:
niche:
evolution:
Why are homologous structures viewed as evidence of evolution? Give two examples of a homologous structure.
Taxonomy is the ordering and naming of species within the biological world. Recall that Linnaeus formulated the basic taxonomy still used in biology. The classification has a series of categories to classify organisms.
Complete the categories in correct order:
Kingdom – Phylum –…
Write down a memory trick to help you remember the categories in order:
List the five kingdoms of life (placing all bacteria/ archea in one kingdom) and list the defining characteristics of each group:
What do the two names, Homo sapien, represent?
This chapter includes the most basic organisms, the monerans. These organisms lack organelles and a nucleus (making them prokaryotes) and are unicellular. This group includes bacteria. Correctly, the group should be divided into eubacteria and archea.
Define the following terms:
parasite:
pathogen:
autotroph:
heterotroph:
antibiotics:
Explain the steps of a viral infection:
In this chapter we also covered viruses, even though they are not usually considered living organisms. Why not?
Describe the basic anatomy of a virus (main parts):
Bacteria Plant Fungi Animal Protist
|
Heterotroph/ Autotroph/ Both |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mulitcellular/ Unicellular |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cell Wall?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prokaryote/ Eukaryote |
|
|
|
|
|
Chapters 23 – 25: Introduction to Botany
Draw a basic flower and label the stamen, pistil, petals and sepals:
Explain three differences between monocots and dicots:
Describe two unique characteristics of each of the following groups of plants:
Bryophytes:
Seedless Vascular:
Gymnosperms:
Angiosperms:
Draw a cross-section of a leaf (pages 558-9) and label the palisades mesophyll, spongy mesophyll, epidermis, stoma and guard cells.
Define:
xylem:
phloem:
fruit:
vegetable:
stomata:
cuticle:
transpiration:
Write the equation for photosynthesis:
Explain what occurs during photosynthesis:
Write the equation for respiration:
Explain the purpose of respiration:
In what organelle does respiration occur?
In what organelle does photosynthesis occur?
Circle all kingdoms that go through respiration: Plantae, Animal, Protists, Fungi, Monera
Circle all kingdoms that go through photosynthesis: Plantae, Animal, Protists, Fungi, Monera
What is the function of chlorophyll?
Fungi and Protists:
How do fungi obtain energy?
What is a lichen?
What are four characteristics of the kingdom Fungi?
Why are Protists sometime known as the classification junkdrawer?
What is the unifying theme of all protists?
Invertebrates:
Complete the following:
Symmetry Gut Body Cavity Example
Sponge
Cnidarian
Roundworms
Annelids
Arthropods
Echinoderms
Verts:
Endothermic? Type of Heart? Example
Fish
Amphibians
Reptiles
Birds/Aves
Mammals
Heart:
What is the differences between arteries, veins and capillaries?
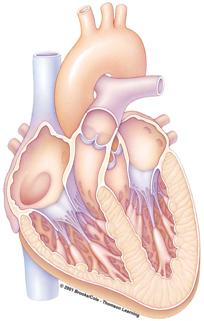
Name the portions of the heart below and circle all portions that move oxygen-rich blood:

![]()

![]()

![]()
Bone and Muscle:
What is the sliding filament theory?
In a sarcomere, what is actin?
In a sarcomere, what is myosin?
Define:
Sarcomere:
Tendon
Ligament
Osteocyte:
Yellow marrow:
Red marrow: