Study Guide for Genetics (Chapter 8)
This chapter begins with a discussion of Gregor Mendel and the history of the science of genetics. Reading this information, you should recognize patterns he discerned, but our test is strictly problem-solving. Very few questions will be in multiple choice format- most will be punnett squares-type problems. Be able to solve the following:
1) A purple-flowered pea plant (heterozygous) is crossed with a white-flowered pea plant (homozygous).
What are the possible offspring and the likelihood of each?
2) A woman is heterozygous for colorblindedness and her husband is not colorblind. The trait is a sex-linked recessive trait.
What is the probability one of their sons will be colorblind?
What is the probability one of their daughters will be colorblind?
3) A man is blood type 0 (ii) and his wife is blood type B (IBIB).
What are the possible blood types of their children and the probability of each?
4) A plant is tall with green peas (AABb) and is crossed with a plant that is dwarf with yellow peas (aabb).
Out of 16 offspring, how many will be tall, green? dwarf, green? tall, yellow? dwarf, yellow?
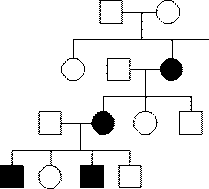
5) In the following pedigree, is the trait recessive or dominant? Explain:

6) Know these terms: heterozygous, homozygous, genotype, phenotype, dominant, recessive, nondisjunction, karyotype, chromosome, dihybrind cross, sex-linked trait, autosome, pedigree.
Answers:
1. 50% purple, 50% white
2. Sons - 50% colorblind Daughters - 0% colorblind
3. 100% type B
4. Tall, Green 8/16
Dwarf, Green 0/16
Tall, Yellow 8/16
Dwarf, Yellow 0/16
5. Recessive because it skipped a generation.
6. Look these up in your textbook or notes.